Africa: Maps, Countries, and Cultural Richness
Maps of Africa and Maps of African Countries
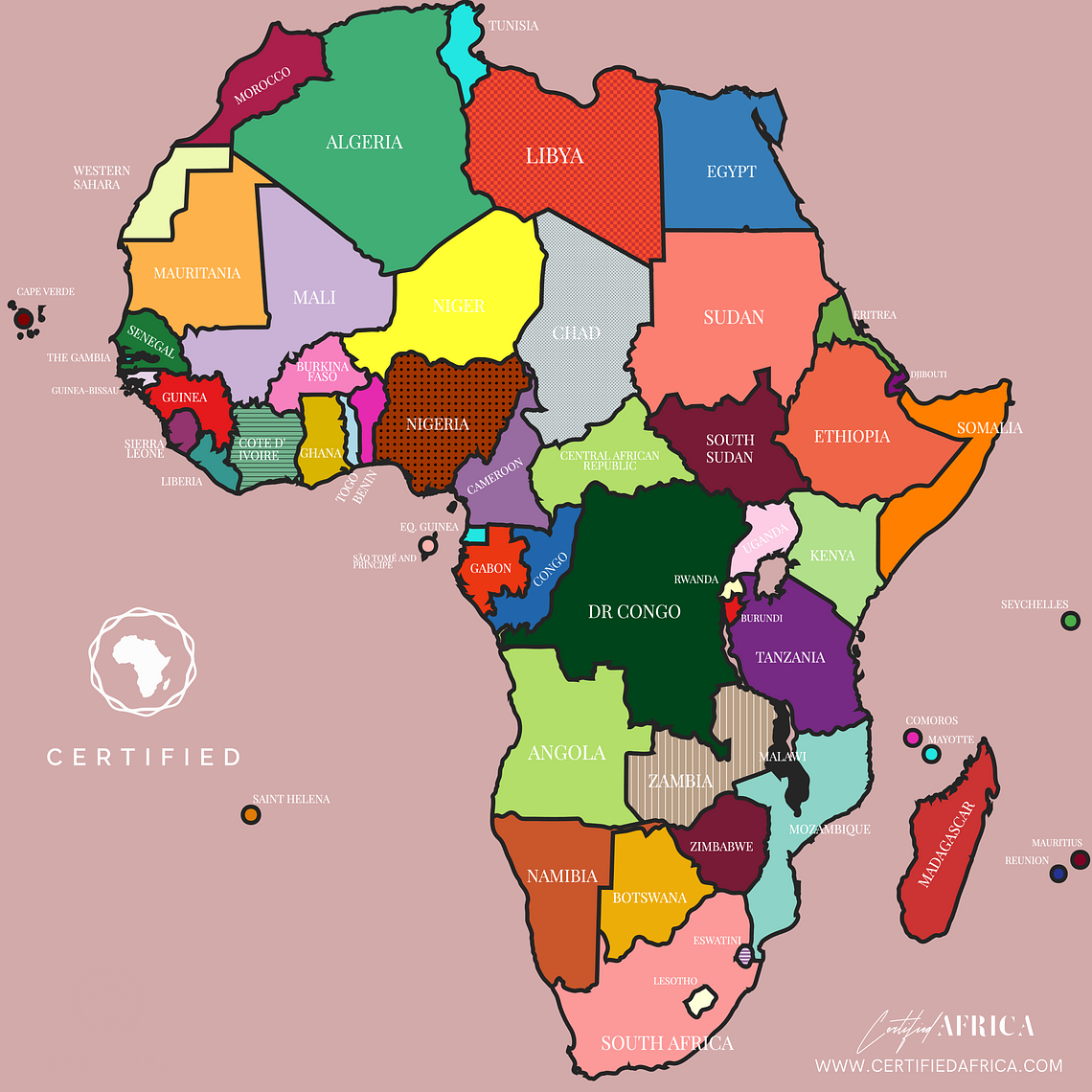
Posted on Thu 20 Mar 2025 · by Certified Africa
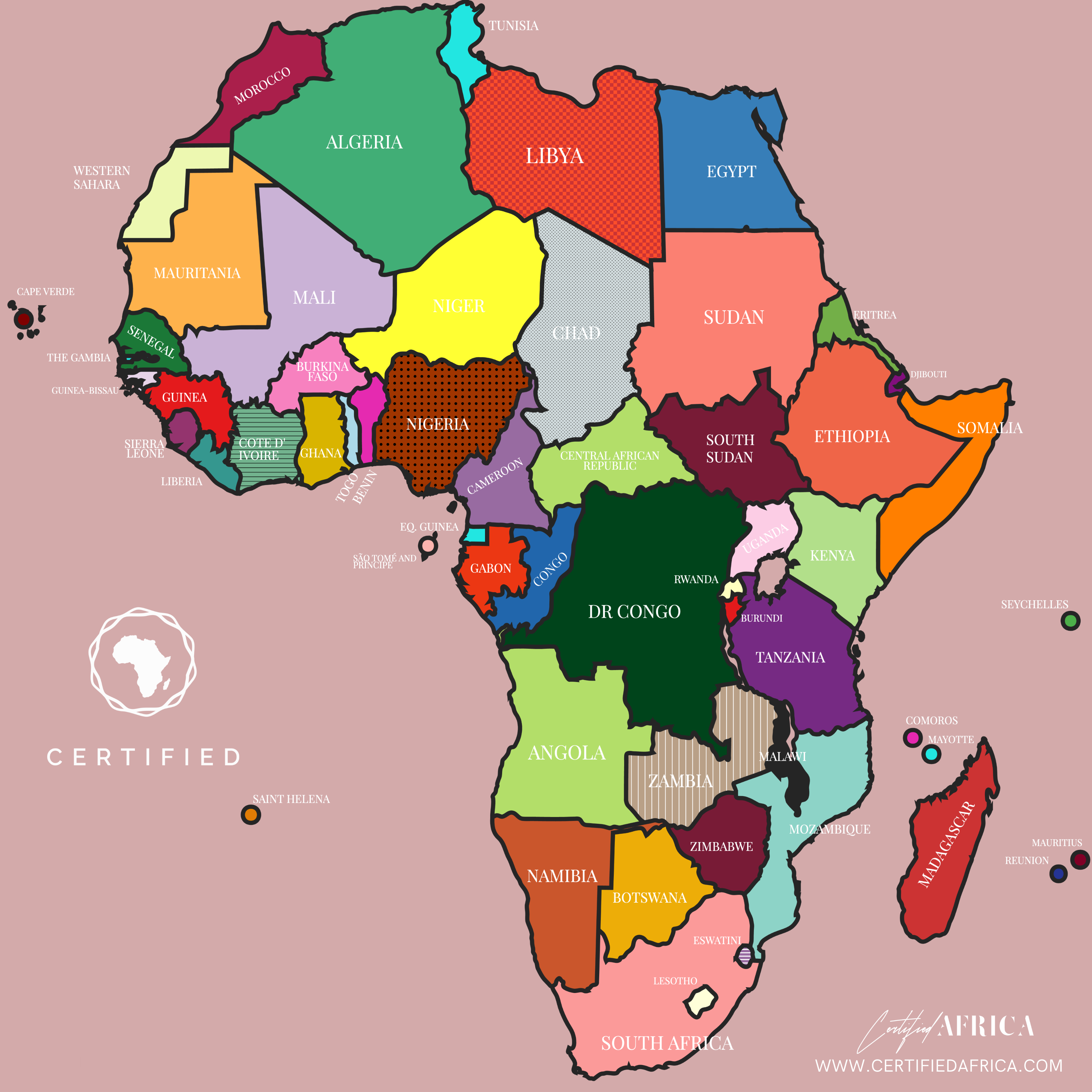
Africa, the second-largest continent on Earth, is a tapestry of diverse cultures, rich histories, and stunning landscapes. With 54 recognized countries, each possessing unique characteristics, Africa is not just a landmass; it is a vibrant collection of stories, traditions, and natural resources that have shaped its identity over millennia. This article delves into the geographical layout of Africa, its countries, and the historical significance that underpins its development and global importance.
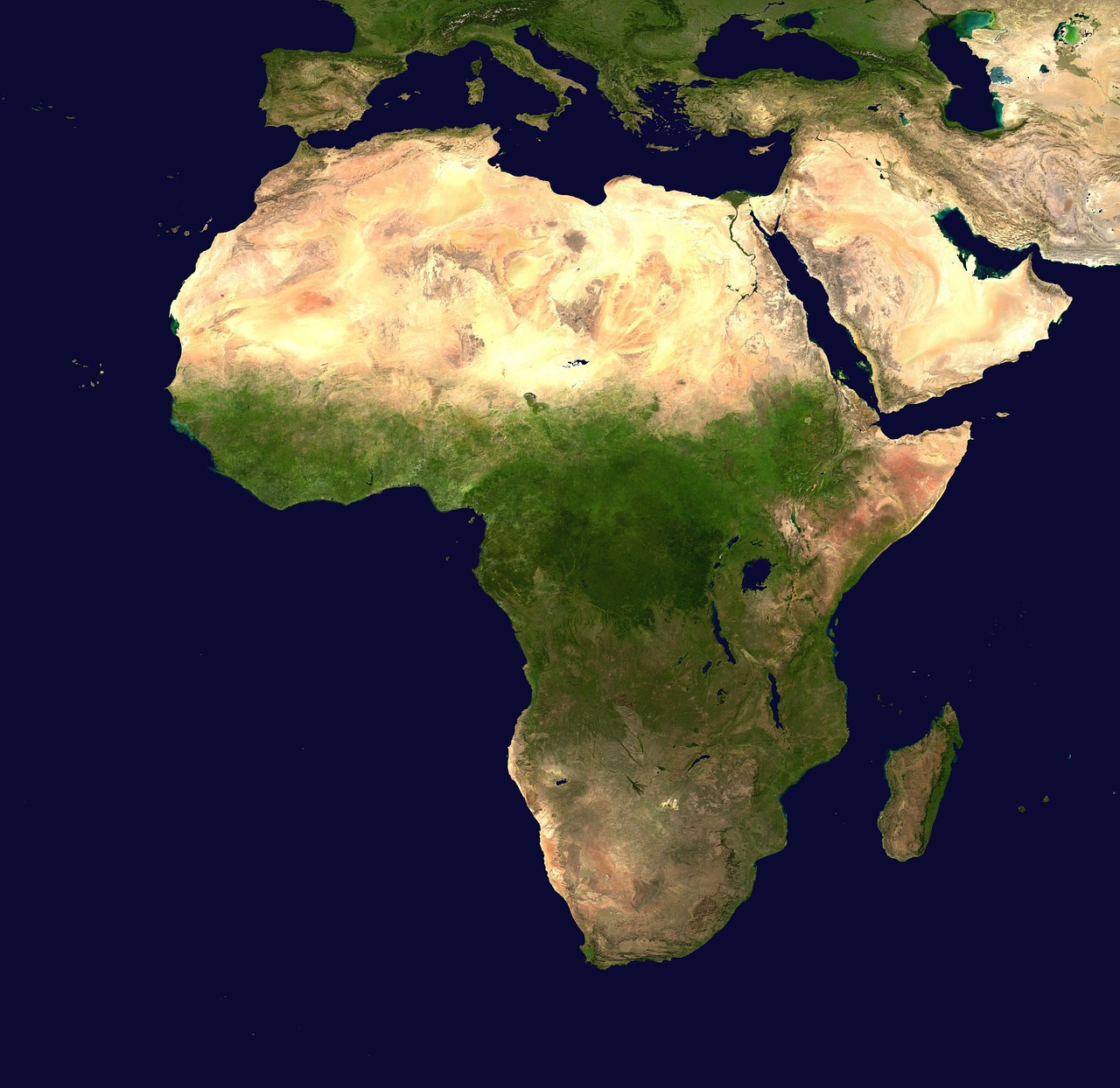
The Geographical Landscape of Africa
Overview of Africa's Geography
Africa covers approximately 30.2 million square kilometers, making it the second-largest continent after Asia. The continent is bordered by several bodies of water, including the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the Indian Ocean to the southeast.
- Regions: Africa is typically divided into five major regions:
- North Africa: Comprising countries like Egypt and Morocco, this region is characterized by its desert landscapes and Mediterranean climate.
- West Africa: Known for its cultural diversity, it includes nations such as Nigeria and Ghana.
- East Africa: Home to iconic wildlife and landscapes, including Kenya and Tanzania.
- Central Africa: Rich in biodiversity, it features countries like the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- Southern Africa: Encompassing nations like South Africa and Namibia, this region is known for its varied topography and rich resources.
Political and Physical Maps of Africa
Political maps of Africa showcase the boundaries of its countries, highlighting capitals and major cities. Conversely, physical maps reveal the continent's topographical features, such as mountains, rivers, and deserts.
- Major Physical Features:
- The Sahara Desert: The largest hot desert in the world, covering much of North Africa.
- The Nile River: Recognized as the longest river globally, it flows through several countries, providing vital resources.
- Mount Kilimanjaro: The highest peak in Africa, located in Tanzania, is a significant landmark.
Satellite Imagery and Technological Exploration
Modern technology has enabled us to explore Africa from a new perspective. Tools like Google Earth allow users to view satellite images, providing detailed insights into the continent's geography. This technology reveals urban areas, natural landscapes, and even the intricate patterns of human habitation.
Population
As of 2025, the population of Africa is estimated to be around 1.4 to 1.5 billion people, according to projections by organizations like the United Nations (UN) and the World Bank. Africa is the second-most populous continent after Asia and has the youngest population globally, with a median age of about 19.7 years.
Key Population Statistics for Africa (2025 Estimates)
Total Population: ~1.4–1.5 billion.
Population Growth Rate: Africa has the highest population growth rate in the world, at around 2.5% annually.
-
Most Populous Countries:
Nigeria: ~230 million (Africa’s most populous country).
Ethiopia: ~130 million.
Egypt: ~110 million.
Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC): ~110 million.
South Africa: ~65 million.
Factors Driving Population Growth
High Birth Rates: Many African countries have high fertility rates, with an average of 4.4 children per woman (compared to the global average of 2.3).
Young Population: Over 60% of Africa’s population is under the age of 25, contributing to rapid population growth.
Improving Healthcare: Advances in healthcare have reduced infant mortality rates and increased life expectancy.
Urbanization: Rapid urbanization is leading to population concentration in cities like Lagos, Cairo, and Kinshasa.
Projections for the Future
By 2050, Africa’s population is expected to double, reaching 2.5 billion people.
By 2100, Africa could be home to 4.3 billion people, making up 40% of the global population.
Implications of Population Growth
-
Economic Opportunities:
A young, growing population can drive economic growth through a larger workforce and consumer base.
-
Challenges:
Pressure on resources, infrastructure, and healthcare systems.
Need for job creation and education to harness the potential of the youth population.
A Historical Overview of Africa
Ancient Civilizations
Africa's historical narrative is rich and multifaceted, beginning with some of the earliest civilizations known to humanity.
- Ancient Egypt: Flourishing from around 3100 BCE, this civilization is renowned for its monumental architecture, including the pyramids, and significant advancements in writing, mathematics, and governance.
- The Kingdom of Kush: Located in present-day Sudan, this kingdom was a powerful rival to Egypt, known for its wealth and cultural achievements.
- The Axum Empire: Emerging in the 1st century CE in what is now Ethiopia, it was one of the first major Christian kingdoms and a hub of trade.
Medieval Kingdoms and Empires
The medieval period saw the rise of powerful empires that dominated trade and culture across the continent.
- Mali Empire: From 1235 to 1670, this empire became one of the wealthiest in history, largely due to its gold trade and the legendary ruler Mansa Musa.
- Songhai Empire (1464–1591): Following the Mali Empire, it became a center for trade and Islamic scholarship, significantly influencing West Africa.
- Great Zimbabwe (11th–15th century): Known for its impressive stone structures, this kingdom thrived from the 11th to the 15th century in Southern Africa.
Transatlantic Slave Trade (15th–19th Century)
Millions of Africans were forcibly taken from West and Central Africa to the Americas and the Caribbean as part of the transatlantic slave trade.
This period had a devastating impact on African societies and economies.
The Impact of Colonialism
The late 19th century marked a significant turning point in Africa's history, as European powers began to colonize the continent during the Scramble for Africa. This period led to the exploitation of Africa’s resources and the imposition of foreign rule, resulting in lasting political and economic challenges.
Independence Movements
The mid-20th century saw a wave of independence movements across Africa, as nations sought to reclaim their sovereignty. Leaders like Kwame Nkrumah in Ghana and Nelson Mandela in South Africa became symbols of resistance and hope for many.
The Rich Tapestry of African Countries
List of African Countries and African Capitals
Africa is home to 54 recognized sovereign states, each with its unique cultural and geographical identity. Here’s a breakdown of countries by region:
1. North Africa
North Africa is characterized by its proximity to the Mediterranean Sea and the Sahara Desert. The region has strong cultural ties to the Arab world.
Algeria (Capital: Algiers)
Egypt (Capital: Cairo)
Libya (Capital: Tripoli)
Morocco (Capital: Rabat)
Sudan (Capital: Khartoum)
Tunisia (Capital: Tunis)
Western Sahara (Disputed territory, claimed by Morocco)
2. West Africa
West Africa is known for its diverse cultures, vibrant music, and rich history, including the transatlantic slave trade.
Benin (Capital: Porto-Novo)
Burkina Faso (Capital: Ouagadougou)
Cabo Verde (Capital: Praia)
Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast) (Capital: Yamoussoukro)
Gambia (Capital: Banjul)
Ghana (Capital: Accra)
Guinea (Capital: Conakry)
Guinea-Bissau (Capital: Bissau)
Liberia (Capital: Monrovia)
Mali (Capital: Bamako)
Mauritania (Capital: Nouakchott)
Niger (Capital: Niamey)
Nigeria (Capital: Abuja)
Senegal (Capital: Dakar)
Sierra Leone (Capital: Freetown)
Togo (Capital: Lomé)
3. East Africa
East Africa is famous for its wildlife, stunning landscapes, and the Great Rift Valley.
Burundi (Capital: Gitega)
Comoros (Capital: Moroni)
Djibouti (Capital: Djibouti City)
Eritrea (Capital: Asmara)
Ethiopia (Capital: Addis Ababa)
Kenya (Capital: Nairobi)
Madagascar (Capital: Antananarivo)
Malawi (Capital: Lilongwe)
Mauritius (Capital: Port Louis)
Mozambique (Capital: Maputo)
Rwanda (Capital: Kigali)
Seychelles (Capital: Victoria)
Somalia (Capital: Mogadishu)
South Sudan (Capital: Juba)
Tanzania (Capital: Dodoma)
Uganda (Capital: Kampala)
Zambia (Capital: Lusaka)
Zimbabwe (Capital: Harare)
4. Central Africa
Central Africa is known for its rainforests, rivers, and rich biodiversity.
Angola (Capital: Luanda)
Cameroon (Capital: Yaoundé)
Central African Republic (Capital: Bangui)
Chad (Capital: N'Djamena)
Democratic Republic of the Congo (Capital: Kinshasa)
Republic of the Congo (Capital: Brazzaville)
Equatorial Guinea (Capital: Malabo)
Gabon (Capital: Libreville)
São Tomé and Príncipe (Capital: São Tomé)
5. Southern Africa
Southern Africa is known for its diverse landscapes, including deserts, savannas, and coastal regions.
Botswana (Capital: Gaborone)
Eswatini (Swaziland) (Capital: Mbabane)
Lesotho (Capital: Maseru)
Namibia (Capital: Windhoek)
South Africa (Capitals: Pretoria, Cape Town, Bloemfontein)
Key Facts About African Countries
- Largest Country by Area: Algeria (2.38 million sq km).
- Smallest Country by Area: Seychelles (451 sq km).
- Most Populous Country: Nigeria (over 223 million people).
- Least Populous Country: Seychelles (approx. 100,000 people).
- Richest Country by GDP: Nigeria.
- Poorest Country by GDP: Burundi.
Cultural Diversity and Languages
The cultural richness of Africa is reflected in its languages, traditions, and customs. Over 2,000 languages are spoken across the continent, with major languages including Arabic, Swahili, Hausa, Yoruba, and Amharic. Each country boasts its unique cultural practices, festivals, and culinary traditions.
Natural Resources of Africa
Africa is incredibly rich in natural resources, which have played a significant role in its history and continue to shape its economy today. Here’s an overview of Africa’s key resources:
Mineral Wealth
Africa is incredibly rich in natural resources, which have historically played a pivotal role in its economy and global trade.
- Gold: South Africa is a leading producer, with Ghana and Mali also contributing significantly to global gold markets.
- Diamonds: Botswana stands out as the largest producer by value, while South Africa and the Democratic Republic of the Congo hold substantial reserves.
Copper: Zambia and the DRC are major copper producers.
Cobalt: The DRC produces over 70% of the world’s cobalt, a key component in batteries for electric vehicles.
- Platinum: Approximately 80% of the world’s platinum reserves are found in South Africa.
Energy Resources
The continent is also rich in energy resources, including fossil fuels and renewable energy potential.
- Oil: Nigeria is Africa's largest oil producer, followed by Angola and Libya, significantly impacting the global oil market.
Uranium:Niger and Namibia are major producers of uranium, used in nuclear energy.
Natural Gas: Algeria and Nigeria possess vast reserves, contributing to energy supplies in Europe and beyond.
- Renewable Energy: With abundant sunlight and wind, Africa has immense potential for solar and wind energy production, positioning itself as a future leader in renewable resources.
Wildlife and Biodiversity
Africa is home to some of the world’s most iconic wildlife, including the Big Five (lion, leopard, elephant, rhino, and buffalo).
National parks and reserves, such as the Serengeti (Tanzania) and Kruger National Park (South Africa), attract millions of tourists annually.
Agricultural Abundance
Africa's diverse climates allow for a wide range of agricultural products.
- Cocoa and Coffee: Ivory Coast and Ghana are the top producers of cocoa beans, while Ethiopia is renowned for its coffee.
- Tea and Palm Oil: Kenya is among the largest tea exporters, and Nigeria and Ghana are key producers of palm oil.
Environmental Challenges and Opportunities
Environmental Issues
While Africa is rich in resources, it also faces significant environmental challenges.
- Deforestation: Rapid deforestation due to agriculture and logging threatens biodiversity and contributes to climate change.
- Resource Exploitation: The "resource curse" affects many countries, where wealth from natural resources leads to corruption and inequality.
- Climate Change: Vulnerable to climate impacts, many African nations are grappling with droughts, floods, and shifting weather patterns.
Opportunities for Sustainable Development
Despite these challenges, Africa has opportunities for sustainable development.
- Renewable Energy Initiatives: Countries are investing in renewable energy projects to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and combat climate change.
- Ecotourism: The continent's rich biodiversity and natural beauty present opportunities for ecotourism, promoting conservation while supporting local economies.
- Agricultural Innovation: Advancements in agricultural practices can enhance food security and sustainability, making better use of the continent's vast arable land.
Development in Africa
Economic Growth and Innovation
Rising Economies: Countries like Ethiopia, Ghana, and Rwanda are among the fastest-growing economies in the world.
Tech Hubs: Cities like Lagos (Nigeria), Nairobi (Kenya), and Cape Town (South Africa) are emerging as major tech hubs, with thriving startup ecosystems.
Mobile Money: Kenya’s M-Pesa revolutionized mobile banking, providing financial services to millions of unbanked people.
Advances in Healthcare
Fighting Diseases: Africa has made significant progress in combating diseases like HIV/AIDS, malaria, and tuberculosis. For example, new HIV infections have declined by 43% since 2010.
Ebola Response: African countries, with international support, have effectively managed Ebola outbreaks through rapid response and community engagement.
Healthcare Innovations: Countries like Rwanda have implemented universal healthcare systems, improving access to medical services.
Education and Youth Empowerment
Increased School Enrollment: Primary school enrollment rates have risen significantly across the continent, with countries like Rwanda and Ghana achieving near-universal primary education.
STEM Education: Initiatives like the African Institute for Mathematical Sciences (AIMS) are training the next generation of scientists and innovators.
Youth Entrepreneurship: Programs like the Tony Elumelu Foundation are empowering young African entrepreneurs with funding and mentorship.
Renewable Energy and Sustainability
Solar Power: Africa is a leader in solar energy, with projects like the Noor Ouarzazate Solar Complex in Morocco, one of the largest solar farms in the world.
Wind Energy: Countries like Kenya and South Africa are investing in wind energy, with projects like the Lake Turkana Wind Power Project.
Green Initiatives: Rwanda is known as one of the cleanest countries in the world, with initiatives like banning plastic bags and promoting reforestation.
Political Stability and Governance
Democratic Progress: Many African countries have made strides in democracy and governance. For example, Ghana and Botswana are often cited as models of stable democracies.
Women in Leadership: Africa has some of the highest rates of female political representation globally. Rwanda leads the world with over 60% of parliamentary seats held by women.
Peacekeeping: African nations contribute significantly to UN peacekeeping missions, promoting stability in conflict zones.
Cultural and Creative Industries
Nollywood: Nigeria’s film industry, Nollywood, is the second-largest in the world by volume, producing thousands of films annually and creating millions of jobs.
Afrobeats: African music genres like Afrobeats and Amapiano are gaining global popularity, with artists like Burna Boy, Wizkid, and Tems winning international awards.
Fashion and Art: African fashion designers and artists are gaining global recognition, showcasing the continent’s rich cultural heritage.
Infrastructure Development
Transport Networks: Major infrastructure projects, like the Lagos-Ibadan Railway in Nigeria and the Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway, are improving connectivity and trade.
Urban Development: Cities like Kigali (Rwanda) and Nairobi (Kenya) are becoming models of sustainable urban planning.
Digital Infrastructure: The expansion of internet access and mobile networks is driving digital transformation across the continent.
Conservation and Wildlife Protection
Anti-Poaching Efforts: Countries like Kenya and South Africa are implementing successful anti-poaching initiatives to protect endangered species like rhinos and elephants.
National Parks: Africa’s national parks, such as the Serengeti and Kruger, are world-renowned for their biodiversity and conservation efforts.
Community-Based Conservation: Programs like Namibia’s communal conservancies empower local communities to manage and benefit from wildlife resources.
Agricultural Innovation
Food Security: Innovations in agriculture, such as drought-resistant crops and mobile-based farming advice, are improving food security.
Agribusiness: Countries like Ethiopia and Kenya are investing in agribusiness, creating jobs and boosting exports.
Land Restoration: Initiatives like the Great Green Wall aim to combat desertification by planting trees across the Sahel region.
Social Progress and Inclusion
Gender Equality: Many African countries are making progress in gender equality, with initiatives to empower women in education, business, and politics.
Youth Empowerment: Programs like the African Union’s Agenda 2063 focus on harnessing the potential of Africa’s youth for sustainable development.
Community Development: Grassroots organizations are driving positive change in areas like healthcare, education, and environmental sustainability.
Sports and Global Influence
Football (Soccer): African footballers like Mohamed Salah, Sadio Mané, and Samuel Eto’o are global superstars, inspiring millions.
Marathon Running: Kenya and Ethiopia dominate long-distance running, with athletes like Eliud Kipchoge breaking world records.
Olympic Success: African athletes consistently excel in international competitions, bringing pride to the continent.
Tourism and Hospitality
Ecotourism: Countries like Botswana, Namibia, and Tanzania are leaders in ecotourism, promoting conservation and community development.
Cultural Tourism: Africa’s rich cultural heritage, from ancient pyramids to vibrant festivals, attracts millions of tourists annually.
Luxury Travel: Destinations like Seychelles, Mauritius, and South Africa offer world-class luxury travel experiences.
The Role of Tourism in Africa
Ecotourism and Cultural Tourism
Tourism plays a crucial role in Africa's economy, providing income and employment opportunities.
- Wildlife Safaris: Countries like Kenya and Tanzania attract millions of tourists seeking to experience the continent's iconic wildlife, including the "Big Five" (lion, leopard, elephant, rhinoceros, and buffalo).
- Cultural Heritage: Tourists flock to experience Africa's rich cultural heritage, from ancient pyramids in Egypt to vibrant festivals in West Africa.
Challenges and Sustainable Tourism
While tourism provides economic benefits, it also poses challenges.
- Environmental Impact: Unsustainable tourism practices can lead to habitat destruction and pollution.
- Cultural Sensitivity: It is essential for tourists to engage respectfully with local cultures and communities.
Conclusion
Africa is a continent of immense diversity, rich history, and natural wealth. Understanding its geography, cultural richness, and historical significance provides insight into its global importance. As Africa continues to navigate its challenges and opportunities, it remains a vital player on the world stage, offering a wealth of knowledge, resources, and experiences that enrich the global community. By appreciating Africa's complexities, we can foster a deeper understanding and respect for this remarkable continent, paving the way for a brighter future.